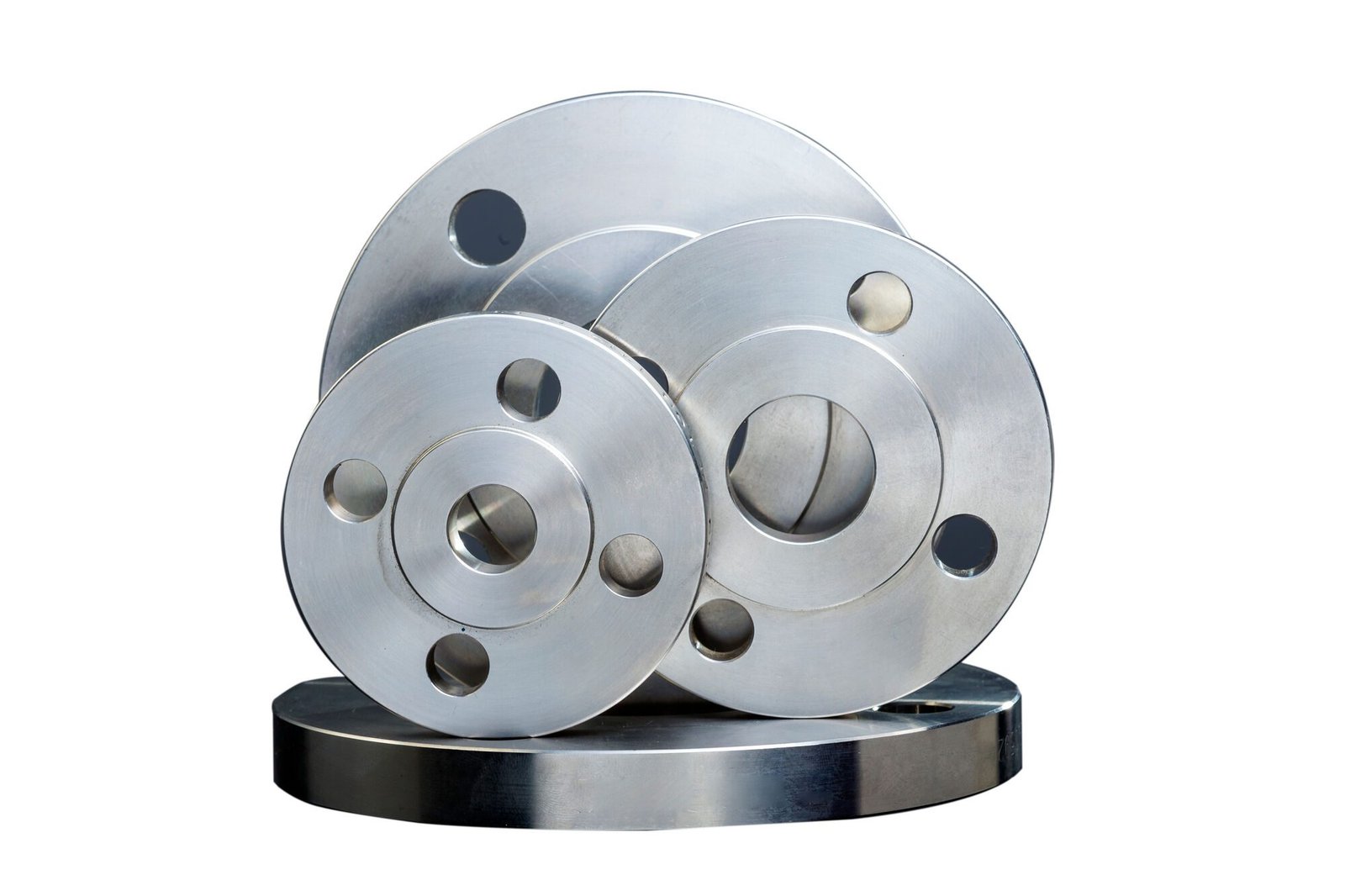
Titanium flanges have become a preferred choice across various industries due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, outstanding corrosion resistance, and ability to perform reliably in harsh environments. Whether used in chemical processing plants, offshore structures, or high-performance aerospace systems, Titanium Flange components are vital for ensuring leak-proof, durable, and efficient piping systems.
However, to fully capitalise on the advantages titanium offers, proper maintenance is essential. In this guide, we’ll explore crucial maintenance tips to enhance the lifespan and performance of your titanium flanges while ensuring safe and efficient system operation.
Why Choose Titanium Flanges?
Before diving into maintenance, let’s quickly recap why Titanium Flanges are valued so highly:
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium naturally forms a protective oxide layer, making it resistant to seawater, acids, and industrial chemicals.
Strength & Durability: Titanium offers high tensile strength while being significantly lighter than steel.
Temperature Resilience: Suitable for both high and cryogenic temperature applications.
Longevity: With proper handling and maintenance, titanium flanges can last decades in critical systems.
Despite these properties, improper maintenance or careless handling can still reduce the life and performance of your titanium components.
1. Handle with Care During Installation
Titanium is a strong material, but it’s not immune to galling or surface damage. During installation:
Use proper torque tools to avoid over-tightening.
Apply anti-galling lubricants or anti-seize compounds where required.
Ensure the gasket material is compatible with titanium to prevent corrosion or leaks.
Use non-metallic or soft grip tools when handling titanium to avoid surface scratches.
Incorrect installation is one of the most common causes of premature flange failure, so proper attention during this stage is crucial.
2. Conduct Routine Inspections
Frequent inspection helps identify early signs of wear, stress, or corrosion that could otherwise escalate into major issues. Key things to look for include:
Surface pitting or discoloration
Signs of fatigue, such as hairline cracks
Gasket misalignment or compression damage
Unusual vibrations or leaks at the flange joint
Schedule inspections based on the service environment — more aggressive chemical or marine settings may require more frequent checks.
3. Monitor for Crevice Corrosion
Although titanium is highly corrosion-resistant, it is still susceptible to crevice corrosion under stagnant conditions in tight spaces, such as the gasket-flange interface.
To prevent this:
Use high-quality gaskets and ensure proper compression to eliminate moisture ingress.
Avoid long periods of stagnation in titanium piping systems.
In marine environments, ensure water does not collect or stagnate around the flange area.
4. Clean Regularly to Avoid Contaminant Buildup
Contaminants such as chloride ions, hydrocarbons, or other aggressive chemicals can accumulate on titanium flanges over time, especially in industrial or coastal settings.
Clean the flange surfaces regularly with mild detergents or solvents compatible with titanium.
Avoid using abrasive pads or steel wool, which can damage the protective oxide layer.
Rinse thoroughly after cleaning to remove any chemical residues.
5. Ensure Proper Bolting and Torque Checks
One of the biggest causes of flange failure is improper bolt tightening or torque loss over time. This can lead to gasket leaks, flange misalignment, or stress fractures.
Check flange bolts periodically for torque retention.
Use titanium-compatible fasteners to avoid galvanic corrosion.
Consider cross-tightening bolts in a star pattern for uniform pressure distribution.
6. Protect Against Galvanic Corrosion
When titanium comes into contact with dissimilar metals in the presence of an electrolyte (like seawater), galvanic corrosion can occur.
To reduce this risk:
Isolate titanium flanges from other metals using non-conductive gaskets or sleeves.
Avoid using carbon steel or aluminum fasteners directly with titanium.
In marine applications, use dielectric coatings or anodic protection where necessary.
7. Store and Transport Flanges Properly
Improper storage and transportation can cause surface contamination or deformation.
Store titanium flanges in clean, dry environments.
Keep them away from greasy or oily substances, which can affect weldability or surface finish.
Use plastic or wooden pallets, and avoid contact with rusty steel surfaces during transit.
8. Document and Schedule Maintenance
Finally, establish a maintenance log that tracks all inspections, repairs, and torque checks. This documentation helps in:
Predicting future maintenance needs
Identifying patterns of wear or system issues
Meeting regulatory and safety standards, especially in aerospace, nuclear, or chemical industries
A proactive maintenance schedule also minimizes downtime and enhances system reliability.
Conclusion
While titanium flanges are among the most durable and resilient components used in piping and structural systems, regular maintenance is essential to preserve their long-term performance. From correct installation techniques to routine inspection and protection against corrosion, every step plays a role in maximizing the lifespan of these critical components.
If you’re sourcing high-quality Titanium Flange products, always work with reliable suppliers who provide technical guidance, product certifications, and maintenance best practices.
By implementing these practical tips, industries can ensure that their titanium flange systems operate safely, efficiently, and reliably for years to come.