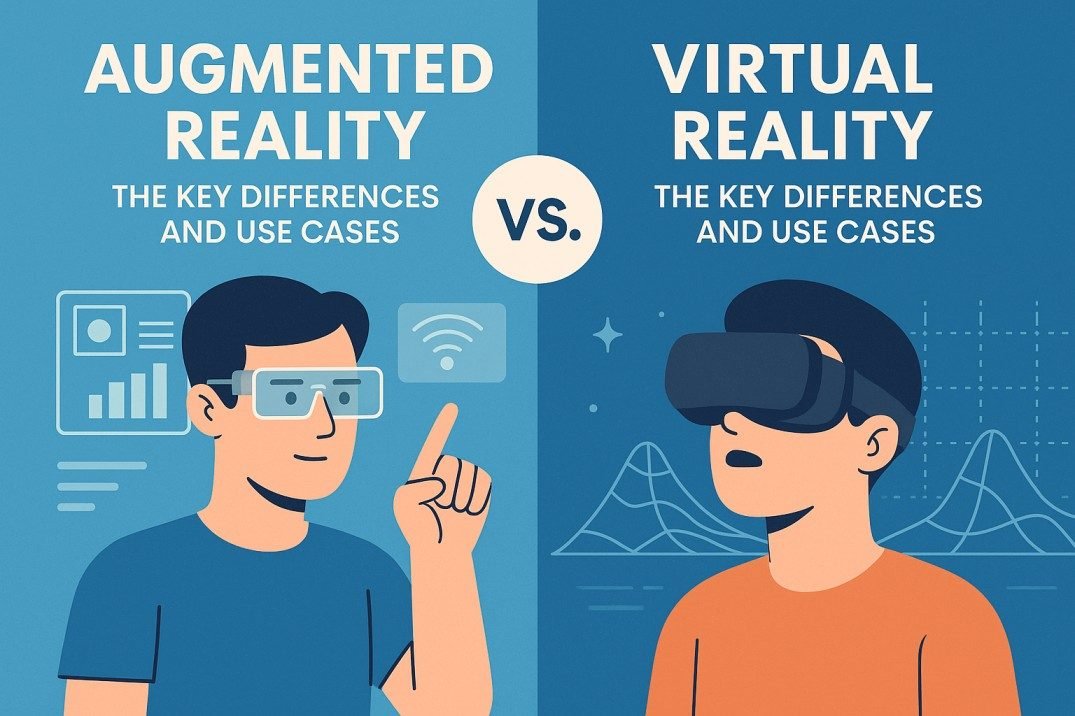
Technology has evolved at lightning speed over the past decade, and two innovations stand out in particular — Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). These technologies are transforming the way we interact with the digital world, from gaming and healthcare to education and business. But what exactly sets them apart? While AR blends digital elements into the real world, VR transports you into a fully digital environment. In this article, we’ll break down the key differences, how each works, and their practical use cases across different industries.
What Is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality enhances your real-world environment by overlaying digital objects, graphics, or information onto it. You can still see and interact with your surroundings, but with added computer-generated visuals. Think of AR as a “digital layer” placed over the real world.
For instance, when you point your phone at your living room and see a virtual couch placed there through an apk — that’s AR in action.
How AR Works
AR uses your device’s camera, sensors, and sometimes GPS to detect real-world objects and blend virtual elements in real-time. Modern smartphones and tablets already have the necessary hardware to support AR, making it easily accessible to users worldwide.
Examples of AR Applications
Snapchat and Instagram filters: Adding fun animations to your face.
Google Maps Live View: Displaying directions directly on the street view.
IKEA Place app: Visualizing furniture in your home before buying.
What Is Virtual Reality (VR)?
Virtual Reality takes immersion to a whole new level. Unlike AR, VR completely replaces the real world with a computer-generated environment. Using a VR headset, you can look around, move, and interact with digital surroundings as if you’re truly there.
How VR Works
VR relies on headsets like the Meta Quest, HTC Vive, or PlayStation VR. These devices track your head movements, adjust visuals accordingly, and often include handheld controllers for interaction. Some systems even use sensors to track your body movements for a more realistic experience.
Examples of VR Applications
VR Training Simulators: Used in industries like aviation, medicine, and manufacturing.
Virtual Tourism: Explore the Eiffel Tower or the Great Wall of China from home.
Education: Students can walk through historical landmarks or the solar system.
Key Differences Between AR and VR
While both technologies create immersive experiences, their goals and approaches differ significantly.
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Enhances the real world | Replaces the real world |
| Equipment | Smartphone or tablet | VR headset required |
| Interaction | Mix of real and digital | Fully digital |
| Accessibility | Easier and cheaper | Requires specialized hardware |
| Use Case | Navigation, education, retail | Gaming, training, virtual meetings |
In simple terms, AR adds to reality, while VR replaces it.
Advantages of AR
Enhances real-world experiences without isolation.
More affordable and widely accessible.
Ideal for interactive marketing and retail experiences.
Advantages of VR
Provides complete immersion for training or simulation.
Excellent for entertainment and education.
Enables exploration of places and experiences that would be impossible in real life.
Use Cases of AR in Real Life
1. Education
Teachers can use AR to bring lessons to life — imagine studying human anatomy with a 3D model projected in front of you.
2. Healthcare
Surgeons use AR to visualize patient anatomy during operations, improving accuracy and safety.
3. Retail and E-Commerce
AR allows shoppers to “try before they buy” by visualizing clothing, accessories, or furniture in real time.
4. Navigation
Apps like Google Maps use AR to display arrows and directions right on the road through your smartphone camera.
Use Cases of VR in Real Life
1. Training and Skill Development
VR is widely used in fields like aviation, engineering, and medicine for safe, realistic practice without real-world risks.
2. Entertainment
From immersive 360° movies to interactive experiences, VR offers a new dimension of storytelling.
3. Real Estate
Potential buyers can take virtual property tours without visiting in person, saving time and money.
4. Mental Health and Therapy
VR is being used to treat anxiety, PTSD, and phobias by simulating controlled environments for exposure therapy.
AR and VR in Business
Businesses are quickly adopting both technologies to engage customers and train employees. For instance, car manufacturers use VR to design prototypes, while retail brands use AR to create interactive shopping experiences. Both technologies are redefining marketing strategies and customer engagement.
Challenges Facing AR and VR
While promising, both come with challenges. AR requires precise tracking and high processing power, while VR demands expensive equipment and sometimes causes motion sickness. However, as technology advances, these hurdles are rapidly being overcome.
The Future of AR and VR
The future is bright for AR and VR. With the rise of 5G, improved sensors, and lighter headsets, both technologies are expected to merge eventually, giving birth to Mixed Reality (MR) — a blend of physical and virtual worlds. Soon, AR glasses could replace smartphones, and VR could become the next big step in digital communication.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality may seem similar, but their applications are distinct. AR enhances your surroundings, while VR transports you to entirely new ones. Whether it’s for education, healthcare, or entertainment, both technologies are reshaping how we interact with the digital world. As they evolve, expect a future where reality and imagination merge seamlessly.
FAQs
1. Can AR and VR work together?
Yes, they can! When combined, they create Mixed Reality (MR), blending both real and virtual worlds for a unified experience.
2. Do AR and VR require the same equipment?
No. AR usually works on phones or tablets, while VR requires specialized headsets.
3. Which is more affordable, AR or VR?
AR is generally cheaper since it runs on existing devices like smartphones.
4. How is AR used in daily life?
From social media filters to online shopping previews, AR is already part of everyday tech experiences.
5. What’s the biggest challenge for VR adoption?
The main barriers are cost, comfort, and the need for high-quality hardware for a truly immersive experience.